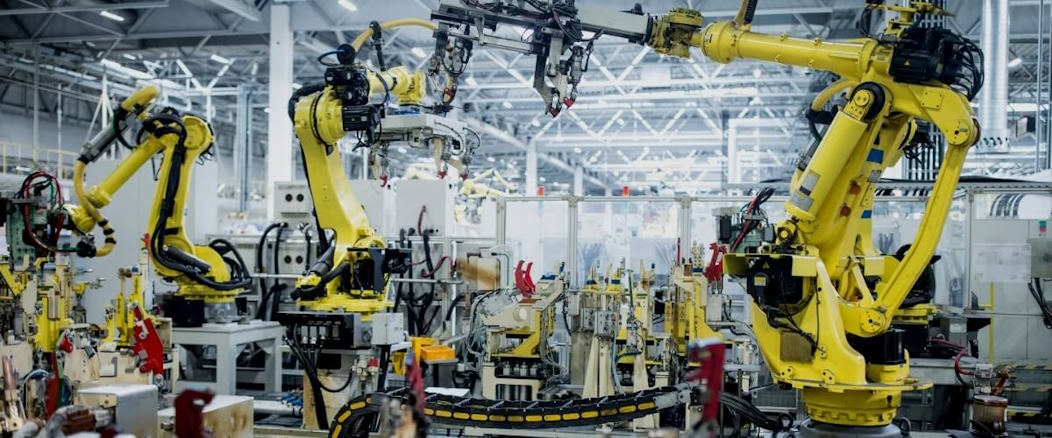

Production plants are the beating heart of Europe’s industrial landscape, where innovation, efficiency, and craftsmanship merge to bring forth the products that power economies and shape our daily lives. These plants are the hidden heroes, often operating behind closed doors, but their impact is felt far and wide. In this article, we will peel back the curtain and delve into the secrets of European production plants, unveiling the intricate processes, advanced technologies, and skilled workforce that make them the driving force of the continent’s industry.
Precision Machining and Robotics
At the core of many production plants lies the art of precision machining. Highly skilled machinists operate state-of-the-art CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines capable of accurately shaping raw materials. These machines, guided by complex algorithms and computer-aided design, produce intricate components that are the building blocks of various industries, from automotive to aerospace. Complementing this precision is the increasing integration of robotics, where automated systems take on repetitive tasks, ensuring consistent quality and freeing up human workers for more complex and creative endeavors.
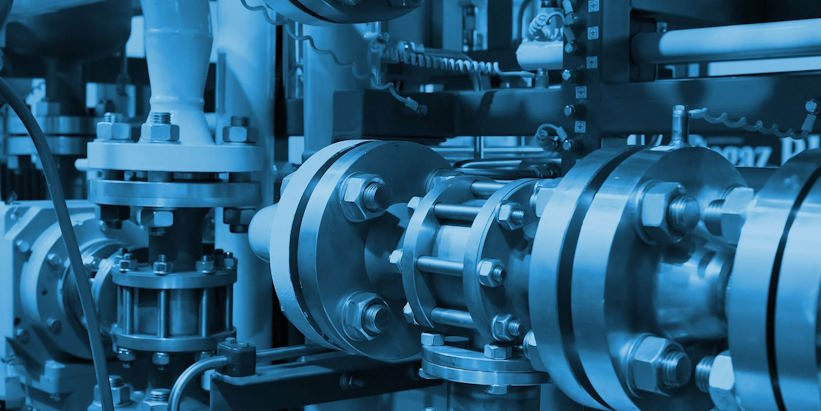
Advanced Assembly Lines
Production plants are often a symphony of meticulously designed assembly lines, where parts and components come together to form the final product. These lines are a testament to efficient logistics and workflow optimization. They incorporate conveyor belts, robotic arms, and sophisticated tracking systems to guide each item through a carefully choreographed process. The goal is to minimize downtime, reduce errors, and achieve high throughput without compromising quality. The continuous improvement of these assembly lines is a never-ending quest as plant managers analyze data, experiment with layout configurations, and introduce lean manufacturing principles to achieve optimal efficiency.
Digitalization and the Internet of Things (IoT)
The rise of Industry 4.0 has transformed production plants into digital ecosystems. Sensors embedded in machines and equipment collect real-time data, enabling proactive maintenance and optimizing operations. This connectivity extends beyond the plant’s boundaries, integrating suppliers and customers into a seamless supply chain network. Through the Internet of Things (IoT), production plants can remotely monitor inventory levels, predict demand, and automate reordering processes. This digital integration ensures just-in-time production, reduces waste, and streamlines the entire value chain.

Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
European production plants are at the forefront of sustainable manufacturing practices. Energy efficiency initiatives, such as intelligent lighting systems, energy recovery systems, and optimized equipment, help minimize environmental impact and reduce operating costs. Renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, are increasingly powering these plants, further reducing carbon footprints. Waste management strategies focus on recycling and circular economy principles, where by-products or waste materials from one process become inputs for another. These sustainable practices demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship while enhancing long-term economic viability.
Skilled Workforce and Continuous Learning
Behind cutting-edge technologies and automated systems, a skilled workforce remains the backbone of European production plants. These individuals bring engineering, machining, programming, and quality control expertise. They continuously adapt to new technologies and undergo training to operate and maintain sophisticated machinery. Beyond technical skills, a culture of continuous learning and problem-solving is fostered, encouraging employees to collaborate, innovate, and contribute to the overall improvement of the plant’s operations.
 Our team of professionals specializes in developing tailored strategies and implementing effective solutions to streamline your business operations and enhance factory production. We believe that a well-organized and optimized workflow is the foundation for achieving operational excellence and improving overall productivity.
Our team of professionals specializes in developing tailored strategies and implementing effective solutions to streamline your business operations and enhance factory production. We believe that a well-organized and optimized workflow is the foundation for achieving operational excellence and improving overall productivity.